| Znav | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
On this page:
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Interface Inheritance
Interfaces support inheritance. For example, we could extend our world-time server to support the concept of an alarm clock:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface AlarmClock extends Clock {
idempotent TimeOfDay getAlarmTime();
idempotent void setAlarmTime(TimeOfDay alarmTime)
throws BadTimeVal;
};
{zcode} |
The semantics of this are the same as for C++ or Java: AlarmClock is a subtype of Clock and an AlarmClock proxy can be substituted wherever a Clock proxy is expected. Obviously, an AlarmClock supports the same getTime and setTime operations as a Clock but also supports the getAlarmTime and setAlarmTime operations.
Multiple interface inheritance is also possible. For example, we can construct a radio alarm clock as follows:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface Radio {
void setFrequency(long hertz) throws GenericError;
void setVolume(long dB) throws GenericError;
};
enum AlarmMode { RadioAlarm, BeepAlarm };
interface RadioClock extends Radio, AlarmClock {
void setMode(AlarmMode mode);
AlarmMode getMode();
};
{zcode} |
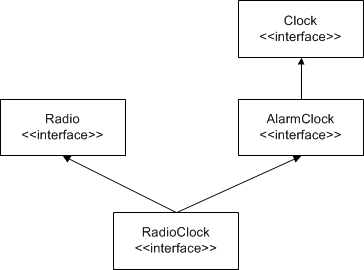
RadioClock extends both Radio and AlarmClock and can therefore be passed where a Radio, an AlarmClock, or a Clock is expected. The inheritance diagram for this definition looks as follows:
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Inheritance diagram for
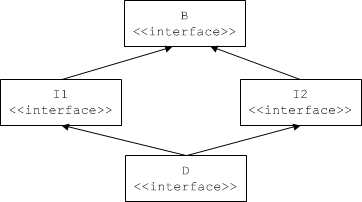
RadioClock.Interfaces that inherit from more than one base interface may share a common base interface. For example, the following definition is legal:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface B { /* ... */ };
interface I1 extends B { /* ... */ };
interface I2 extends B { /* ... */ };
interface D extends I1, I2 { /* ... */ };
{zcode} |
This definition results in the familiar diamond shape:
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Diamond-shaped inheritance.
| Ztop |
|---|
Interface Inheritance Limitations
If an interface uses multiple inheritance, it must not inherit the same operation name from more than one base interface. For example, the following definition is illegal:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface Clock {
void set(TimeOfDay time); // set time
};
interface Radio {
void set(long hertz); // set frequency
};
interface RadioClock extends Radio, Clock { // Illegal!
// ...
};
{zcode} |
This definition is illegal because RadioClock inherits two set operations, Radio::set and Clock::set. The Slice compiler makes this illegal because (unlike C++) many programming languages do not have a built-in facility for disambiguating the different operations. In Slice, the simple rule is that all inherited operations must have unique names. (In practice, this is rarely a problem because inheritance is rarely added to an interface hierarchy "after the fact". To avoid accidental clashes, we suggest that you use descriptive operation names, such as setTime and setFrequency. This makes accidental name clashes less likely.)
| Ztop |
|---|
Implicit Inheritance from Object
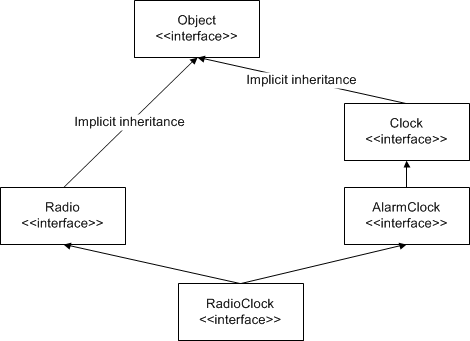
All Slice interfaces are ultimately derived from Object. For example, the inheritance hierarchy would be shown more correctly as:
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Implicit inheritance from
Object.Because all interfaces have a common base interface, we can pass any type of interface as that type. For example:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface ProxyStore {
idempotent void putProxy(string name, Object* o);
idempotent Object* getProxy(string name);
};
{zcode} |
Object is a Slice keyword (note the capitalization) that denotes the root type of the inheritance hierarchy. The ProxyStore interface is a generic proxy storage facility: the client can call putProxy to add a proxy of any type under a given name and later retrieve that proxy again by calling getProxy and supplying that name. The ability to generically store proxies in this fashion allows us to build general-purpose facilities, such as a naming service that can store proxies and deliver them to clients. Such a service, in turn, allows us to avoid hard-coding proxy details into clients and servers.
Inheritance from type Object is always implicit. For example, the following Slice definition is illegal:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface MyInterface extends Object { /* ... */ }; // Error!
{zcode} |
It is understood that all interfaces inherit from type Object; you are not allowed to restate that.
Type Object is mapped to an abstract type by the various language mappings, so you cannot instantiate an Ice object of that type.
| Ztop |
|---|
Null Proxies
Looking at the ProxyStore interface once more, we notice that getProxy does not have an exception specification. The question then is what should happen if a client calls getProxy with a name under which no proxy is stored? Obviously, we could add an exception to indicate this condition to getProxy. However, another option is to return a null proxy. Ice has the built-in notion of a null proxy, which is a proxy that "points nowhere". When such a proxy is returned to the client, the client can test the value of the returned proxy to check whether it is null or denotes a valid object.
A more interesting question is: "which approach is more appropriate, throwing an exception or returning a null proxy?" The answer depends on the expected usage pattern of an interface. For example, if, in normal operation, you do not expect clients to call getProxy with a non-existent name, it is better to throw an exception. (This is probably the case for our ProxyStore interface: the fact that there is no list operation makes it clear that clients are expected to know which names are in use.)
On the other hand, if you expect that clients will occasionally try to look up something that is not there, it is better to return a null proxy. The reason is that throwing an exception breaks the normal flow of control in the client and requires special handling code. This means that you should throw exceptions only in exceptional circumstances. For example, throwing an exception if a database lookup returns an empty result set is wrong; it is expected and normal that a result set is occasionally empty.
It is worth paying attention to such design issues: well-designed interfaces that get these details right are easier to use and easier to understand. Not only do such interfaces make life easier for client developers, they also make it less likely that latent bugs cause problems later.
| Ztop |
|---|
Self-Referential Interfaces
Proxies have pointer semantics, so we can define self-referential interfaces. For example:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface Link {
idempotent SomeType getValue();
idempotent Link* next();
};
{zcode} |
The Link interface contains a next operation that returns a proxy to a Link interface. Obviously, this can be used to create a chain of interfaces; the final link in the chain returns a null proxy from its next operation.
| Ztop |
|---|
Empty Interfaces
The following Slice definition is legal:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface Empty {};
{zcode} |
The Slice compiler will compile this definition without complaint. An interesting question is: "why would I need an empty interface?" In most cases, empty interfaces are an indication of design errors. Here is one example:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface ThingBase {};
interface Thing1 extends ThingBase {
// Operations here...
};
interface Thing2 extends ThingBase {
// Operations here...
};
{zcode} |
Looking at this definition, we can make two observations:
Thing1andThing2have a common base and are therefore related.- Whatever is common to
Thing1andThing2can be found in interfaceThingBase.
Of course, looking at ThingBase, we find that Thing1 and Thing2 do not share any operations at all because ThingBase is empty. Given that we are using an object-oriented paradigm, this is definitely strange: in the object-oriented model, the only way to communicate with an object is to send a message to the object. But, to send a message, we need an operation. Given that ThingBase has no operations, we cannot send a message to it, and it follows that Thing1 and Thing2 are not related because they have no common operations. But of course, seeing that Thing1 and Thing2 have a common base, we conclude that they are related, otherwise the common base would not exist. At this point, most programmers begin to scratch their head and wonder what is going on here.
One common use of the above design is a desire to treat Thing1 and Thing2 polymorphically. For example, we might continue the previous definition as follows:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface ThingUser {
void putThing(ThingBase* thing);
};
{zcode} |
Now the purpose of having the common base becomes clear: we want to be able to pass both Thing1 and Thing2 proxies to putThing. Does this justify the empty base interface? To answer this question, we need to think about what happens in the implementation of putThing. Obviously, putThing cannot possibly invoke an operation on a ThingBase because there are no operations. This means that putThing can do one of two things:
- putThing can simply remember the value of
thing. - putThing can try to down-cast to either
Thing1orThing2and then invoke an operation. The pseudo-code for the implementation ofputThingwould look something like this:
The implementation tries to down-cast its argument to each possible type in turn until it has found the actual run-time type of the argument. Of course, any object-oriented text book worth its price will tell you that this is an abuse of inheritance and leads to maintenance problems.Wiki Markup {zcode} void putThing(ThingBase thing) { if (is_a(Thing1, thing)) { // Do something with Thing1... } else if (is_a(Thing2, thing)) { // Do something with Thing2... } else { // Might be a ThingBase? // ... } } {zcode}
If you find yourself writing operations such as putThing that rely on artificial base interfaces, ask yourself whether you really need to do things this way. For example, a more appropriate design might be:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface Thing1 {
// Operations here...
};
interface Thing2 {
// Operations here...
};
interface ThingUser {
void putThing1(Thing1* thing);
void putThing2(Thing2* thing);
};
{zcode} |
With this design, Thing1 and Thing2 are not related, and ThingUser offers a separate operation for each type of proxy. The implementation of these operations does not need to use any down-casts, and all is well in our object-oriented world.
Another common use of empty base interfaces is the following:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{zcode:slice}
interface PersistentObject {};
interface Thing1 extends PersistentObject {
// Operations here...
};
interface Thing2 extends PersistentObject {
// Operations here...
};
{zcode} |
Clearly, the intent of this design is to place persistence functionality into the PersistentObject base implementation and require objects that want to have persistent state to inherit from PersistentObject. On the face of things, this is reasonable: after all, using inheritance in this way is a well-established design pattern, so what can possibly be wrong with it? As it turns out, there are a number of things that are wrong with this design:
- The above inheritance hierarchy is used to add behavior to
Thing1andThing2. However, in a strict OO model, behavior can be invoked only by sending messages. But, becausePersistentObjecthas no operations, no messages can be sent.
This raises the question of how the implementation ofPersistentObjectactually goes about doing its job; presumably, it knows something about the implementation (that is, the internal state) ofThing1andThing2, so it can write that state into a database. But, if so,PersistentObject,Thing1, andThing2can no longer be implemented in different address spaces because, in that case,PersistentObjectcan no longer get at the state ofThing1andThing2.
Alternatively,Thing1andThing2use some functionality provided byPersistentObjectin order to make their internal state persistent. ButPersistentObjectdoes not have any operations, so how wouldThing1andThing2actually go about achieving this? Again, the only way that can work is ifPersistentObject,Thing1, andThing2are implemented in a single address space and share implementation state behind the scenes, meaning that they cannot be implemented in different address spaces.
- The above inheritance hierarchy splits the world into two halves, one containing persistent objects and one containing non-persistent ones. This has far-reaching ramifications:
- Suppose you have an existing application with already implemented, non-persistent objects. Requirements change over time and you find that you now would like to make some of your objects persistent. With the above design, you cannot do this unless you change the type of your objects because they now must inherit from
PersistentObject. Of course, this is extremely bad news: not only do you have to change the implementation of your objects in the server, you also need to locate and update all the clients that are currently using your objects because they suddenly have a completely new type. What is worse, there is no way to keep things backward compatible: either all clients change with the server, or none of them do. It is impossible for some clients to remain "unupgraded". - The design does not scale to multiple features. Imagine that we have a number of additional behaviors that objects can inherit, such as serialization, fault-tolerance, persistence, and the ability to be searched by a search engine. We quickly end up in a mess of multiple inheritance. What is worse, each possible combination of features creates a completely separate type hierarchy. This means that you can no longer write operations that generically operate on a number of object types. For example, you cannot pass a persistent object to something that expects a non-persistent object, even if the receiver of the object does not care about the persistence aspects of the object. This quickly leads to fragmented and hard-to-maintain type systems. Before long, you will either find yourself rewriting your application or end up with something that is both difficult to use and difficult to maintain.
- Suppose you have an existing application with already implemented, non-persistent objects. Requirements change over time and you find that you now would like to make some of your objects persistent. With the above design, you cannot do this unless you change the type of your objects because they now must inherit from
The foregoing discussion will hopefully serve as a warning: Slice is an interface definition language that has nothing to do with implementation (but empty interfaces almost always indicate that implementation state is shared via mechanisms other than defined interfaces). If you find yourself writing an empty interface definition, at least step back and think about the problem at hand; there may be a more appropriate design that expresses your intent more cleanly. If you do decide to go ahead with an empty interface regardless, be aware that, almost certainly, you will lose the ability to later change the distribution of the object model over physical server processes because you cannot place an address space boundary between interfaces that share hidden state.
| Ztop |
|---|
Interface Versus Implementation Inheritance
Keep in mind that Slice interface inheritance applies only to interfaces. In particular, if two interfaces are in an inheritance relationship, this in no way implies that the implementations of those interfaces must also inherit from each other. You can choose to use implementation inheritance when you implement your interfaces, but you can also make the implementations independent of each other. (To C++ programmers, this often comes as a surprise because C++ uses implementation inheritance by default, and interface inheritance requires extra effort to implement.)
In summary, Slice inheritance simply establishes type compatibility. It says nothing about how interfaces are implemented and, therefore, keeps implementation choices open to whatever is most appropriate for your application.
| Ztop |
|---|
See Also
| Zret |
|---|
| Znav | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|